Rapid advancement in artificial intelligence (AI) and the availability of accessible developer tools have made it relatively easy to incorporate sophisticated AI capabilities into applications. In the past two years, we’ve seen countless AI-powered applications launched. At the same time, developers have been discovering how to enhance existing software with conversational interfaces, predictive analytics, automated customer support, and similar features.
The AI boom caught many by surprise, and standards and regulations have taken a while to catch up. But things are now changing. While the establishment of a regulatory landscape looms, industry standards, spearheaded by the EU AI Act, are moving forward to lead the way.
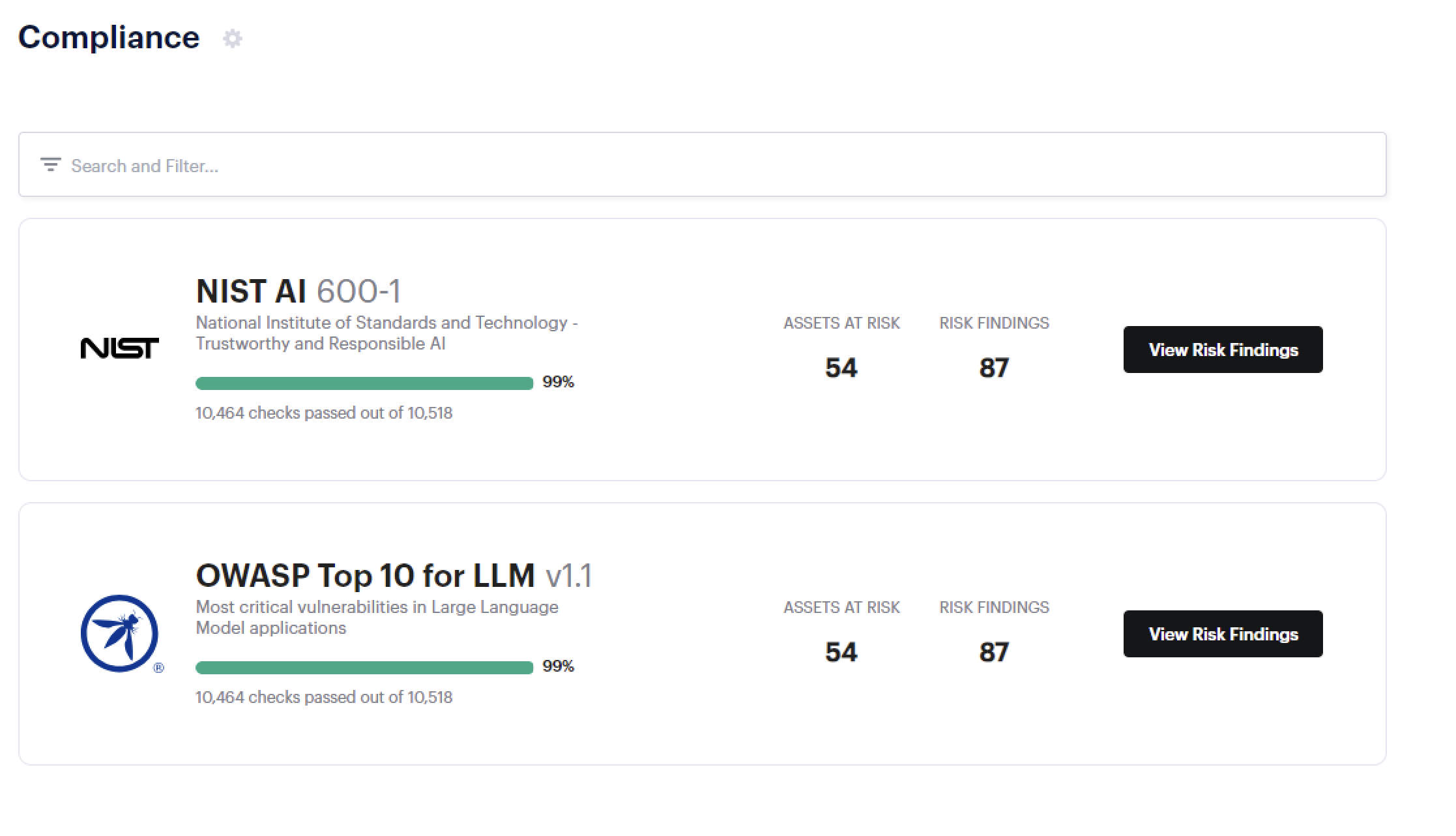
In today’s blog post, we look at two of the main security standards for AI and large language models (LLMs) in application development. We then explain how you can use Prisma Cloud to accelerate and simplify compliance with these standards.
About the OWASP Top 10 for LLM and NIST AI 600-1
The OWASP Top 10 for LLM Applications identifies and ranks the most critical security risks associated with LLM applications. Developed by a global team of nearly 500 experts, this list addresses unique vulnerabilities in LLM systems, including prompt injection, insecure output handling and training data poisoning. It highlights potential security risks when deploying and managing LLMs and offers mitigation strategies to improve the overall security posture of these applications.
NIST AI 600-1, also known as the AI Risk Management Framework developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), offers guidance to help organizations manage risks associated with AI systems. It provides a structured approach for identifying, assessing and mitigating AI-related risks across various domains, including privacy, security and fairness, as well as for addressing concerns such as bias, transparency and accountability in AI systems.
It’s worth noting that while both standards are voluntary, organizations across industries are widely adopting them. For many companies still early in their AI journey, the standards help establish a baseline of secure practices and policies. For those closer to deployment, they help maintain customer trust and a foundation for additional governance efforts.
What about regulations? While the regulatory landscape for AI is still unclear (with near-certain regional differences), complying with industry standards will most likely shorten the time to compliance with binding regulations, whenever they come into play.
Accelerating and Maintaining AI Compliance with Prisma Cloud AI-SPM
Prisma Cloud offers several purpose-built capabilities to improve compliance workflows. To help organizations comply with AI standards, we’ve extended them as built-in features of Prisma Cloud AI-SPM.
Detect Training and Inference Data
Training and inference data is a major risk vector for AI-powered applications. Sensitive information contained in this data can be extracted if cloud resources or user-facing applications are misconfigured. Alternatively, the data that models rely on can be poisoned to create unsafe or low-quality output. Rules such as OWASP LLM06 and LLM03 dictate that controls must be in place to prevent these types of attacks.
Prisma Cloud identifies datasets used for training or inference, including in object storage, documents stores and vector databases, and elsewhere in your cloud environment. It highlights misconfigurations such as publicly readable or publicly writable training datasets, which enable security teams to investigate and remediate the risk and ensure compliance with relevant standards.
Compliance is also baked into Prisma Cloud DSPM’s data classification engine, which automatically detects when a datastore contains data that has significance for a supported compliance framework (e.g., data that falls under the GDPR’s definition of personally identifiable information (PII)).
Discover Deployed AI Models and Inference API Endpoints
Both the OWASP Top 10 and NIST 600-1 require specific guardrails on AI deployments, such as content filtering to prevent model misuse. With the wealth of open source, managed and homegrown models available to developers, however, just knowing what AI model is deployed in what environment can be tricky. Prisma Cloud AI-SPM simplifies the process, automatically finding deployed models and ecosystem components like compute and data resources.
Manage and Prioritize Compliance Risk with Data and AI Posture Management
Once data and models are discovered and classified, Prisma Cloud analyzes security and compliance posture and identifies high-priority issues and misconfigurations. The analysis includes the full context of data at risk of exposure and the part each dataset plays in the AI supply chain (whether used as training or inference data).
With Prisma Cloud, you gain instant visibility into compliance risk, both at a big-picture and granular level. In just a few clicks, you can see the AI compliance frameworks you’re aiming to comply with and drill down into the datastores, datasets or records that put you at risk of a violation.
Example of AI Compliance Risks Covered by Prisma Cloud
Prisma Cloud and other Palo Alto Networks cloud security solutions cover controls required by the OWASP Top 10 for LLM and NIST AI-600-1. The table below gives you an idea of the type of AI security risks covered by Prisma Cloud’s out-of-the-box guardrails.
| Risk | Description | OWASP 1.1 | NIST AI 600-1 |
| Publicly writable training dataset | Fine-tuned or trained models rely on the fidelity and security of training data to ensure that they’re suitable to the organization’s needs. If a training dataset is publicly writable it can be compromised, impacting model output quality or leading to unsafe responses. | LLMO3: Training Data Poisoning
LLM05: Supply Chain Vulnerabilities |
8: Information Integrity
9: Information Security 12: Value Chain and Component Integration |
| Al inference dataset from foreign project | Al applications often rely on retrieval augmented generation (RAG) to produce grounded and accurate results. This mechanism relies on inference datasets that contain the grounding data.
When data is ingested from foreign projects, the application is at risk of inference data poisoning. |
LLM03: Training Data Poisoning
LLM05: Supply Chain Vulnerabilities |
8: Information Integrity
9: Information Security 12: Value Chain and Component Integration |
| Al asset without content filtering | Al deployments often serve end-user-facing applications. In these cases, the best practice calls for robust content filtering policies on model inputs (to prevent unapproved model use or sensitive data sharing) and on outputs (to prevent unsafe or insecure model responses). | LLM01: Prompt Injection
LLM02: Insecure Output Handling |
3: Dangerous, Violent or Hateful Content
9: Information Security 11: Obscene, Degrading or Abusive Content |
Accelerate Your AI Compliance Journey with Prisma Cloud
Prisma Cloud is the only CNAPP that improves your AI security and compliance posture with complete Code to Cloud™ protection. With Prisma Cloud, you can continuously monitor and visualize your compliance with leading AI standards and simplify the process of responding to violations or vulnerabilities.
Leveraging broad multicloud coverage and powerful data-centric capabilities, Prisma Cloud AI-SPM is uniquely designed to identify the latest AI risks and attack paths that can lead to insecure or unsafe usage. These capabilities can then be augmented with additional tools within Palo Alto Networks’ cloud security suite, including Cortex XSOAR for remediation, and with runtime protection tools.
To see how everything comes together, request a Prisma Cloud demo.