Rapid advancements in generative AI have enabled organizations to build powerful applications by integrating foundation models with internal data and systems. The potential rewards are high, but so are the risks — from sensitive data exposure and compliance violations to prompt injection and attacks against deployed applications.
To mitigate AI-related risk, organizations need a comprehensive approach that covers the application lifecycle from data collection to model output. In today’s blog post, we look at the current state of genAI security and how Prisma Cloud by Palo Alto Networks can be used alongside Amazon Bedrock to build, manage and deploy secure, AI-powered applications.
Prisma Cloud AI-SPM (AI security posture management) and Prisma Cloud DSPM (data security posture management) are integrated capabilities that provide visibility, risk analysis and security controls for AI assets and sensitive data across cloud environments.
Amazon Bedrock is a fully managed service that offers access to a range of foundation models and tools for building and deploying generative AI applications securely, including fine-tuning, RAG, developer experience and customization tools. Amazon Bedrock Guardrails, which has recently been made available as a standalone API, adds runtime protection capabilities that, among other things, block harmful content and identify hallucinations in LLM outputs.
Challenges of Securing GenAI as It Matures from Novelty to Feature
As organizations move from experimenting with generative AI to deploying it at scale, three key trends have emerged, each with security implications.
1. Integration with internal data and systems highlights data risk.
“Vanilla” LLMs need to be augmented with proprietary data to create significant enterprise value. To that end, organizations are fine-tuning models on domain-specific data or using techniques like retrieval augmented generation (RAG) to inject relevant information into prompts to create more customized and capable AI assistants.
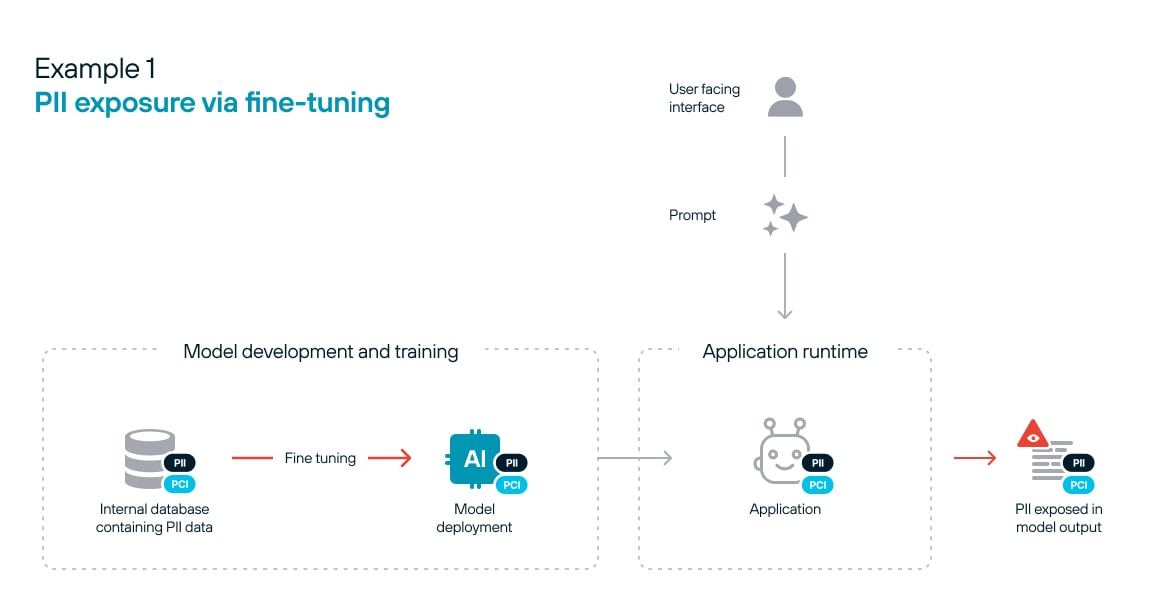
This integration, however, creates new attack surfaces. Sensitive data used for fine-tuning or passed to the model at inference time can inadvertently be exposed in the model's outputs. For example, an LLM fine-tuned on a company's internal documents might leak snippets of confidential information when asked the right prompts. Organizations must meticulously control access to inference data and monitor model inputs and outputs to prevent data exfiltration and comply with data privacy regulations.
Figure 1 illustrates how sensitive data can be exposed by a fine-tuned model. Risk materializes during the fine-tuning process and becomes embedded in the model. The only means to remove the risk after the fact will require redeploying the model.
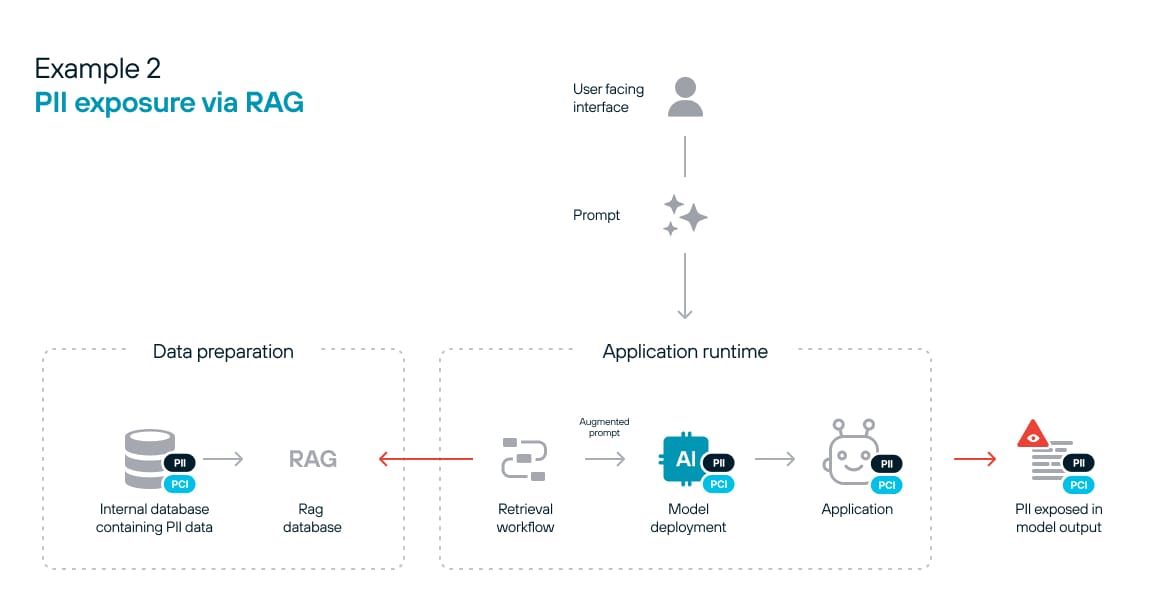
RAG poses another risk of data exposure. The example seen in figure 2 is more straightforward to mitigate than the above example, as the exposure occurs at the “retrieval” stage and is not inherent in the model. Removing sensitive data from the inference data eliminates the risk.
2. Proliferation of models and frameworks complicates effective governance efforts.
The OpenAI API was the only viable option for adding LLM capabilities to applications just a few years ago. Today, developers can choose from a range of open-source foundation models — including specific models tailored for image, speech or video generation. Deployment models have also diversified. In addition to inference APIs offered as SaaS, models can now be deployed in private cloud environments, self-managed infrastructure and, in some cases, locally.
Variety enables developers to choose the most efficient and effective model per task, ultimately reducing costs and increasing quality. But variety also makes life more complicated for security teams.
Shadow AI deployments using unsanctioned models may crop up, making it difficult to assess the overall security posture. The supply chain for models also needs scrutiny. A malicious actor, for example, could publish a backdoored model or dataset aiming to poison downstream models on which it’s trained. Organizations need ways to discover models deployed across their environment and trace their provenance and lineage.
3. The shift from experimentation to production requires new controls.
As companies move beyond developing initial proof of concepts to deploying genAI in production, a new set of application security risks have emerged. Prompt injection attacks, where cleverly crafted text prompts elicit unintended behaviors from a model, have already targeted popular models and AI assistants. Attackers use these techniques to bypass content filters, trick AI systems into accessing unauthorized resources or expose sensitive information via the model's outputs.
To prevent attacks targeting models at runtime, organizations need to proactively identify cases where a model is deployed without adequate safety and security controls (such as output monitoring). Identifying these issues early can mitigate risks that prove harder to catch and prevent once an AI application is in the wild.
Securing LLM-Powered Applications from Data to Runtime with Prisma Cloud and Amazon Bedrock
Amazon Bedrock and Prisma Cloud provide a complete solution to help organizations deploy secure LLM-powered applications — and protect them across the entire lifecycle.
Protecting Data Used for RAG or Fine-Tuning
Protecting the data used to train, fine-tune or augment models is the foundation of secure AI applications. Prisma Cloud DSPM provides comprehensive visibility into your inference data, whether it's stored in S3 buckets, databases or other cloud services. The solution can identify a database containing sensitive customer information being used in RAG workflows such as OpenSearch, for example. This knowledge enables security and compliance teams to weigh in on whether the data should become part of the application’s inference data.
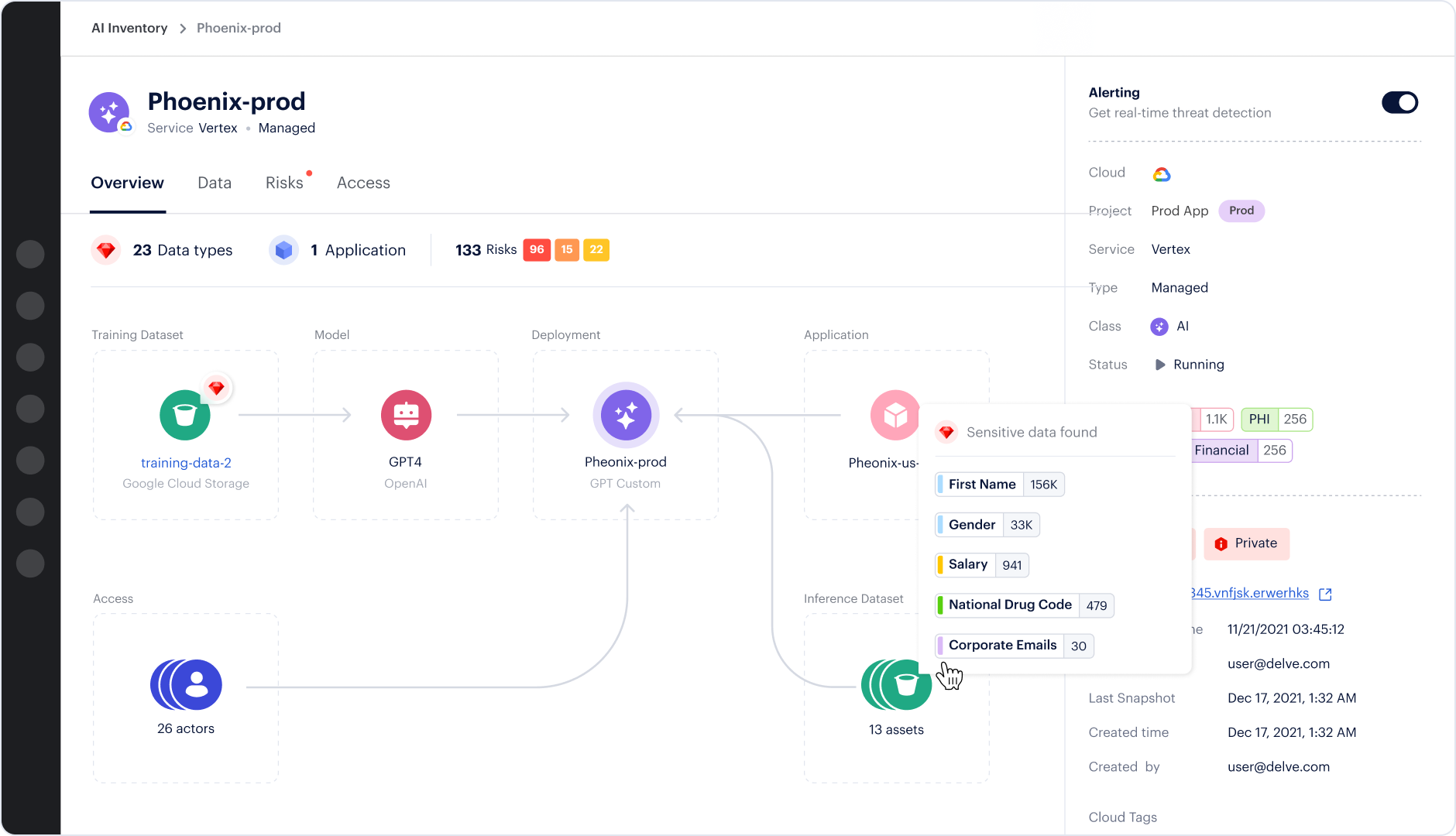
Prisma Cloud goes beyond simple discovery to mapping cloud services and identities with access to particular data sources. This context helps security teams prioritize their efforts, enabling them to focus initially on protecting the most sensitive and widely accessible data. Amazon Bedrock serves as a centralized platform for RAG operations, providing clear visibility into which services are being used for inference and ensuring that access to internal data is properly managed and logged.
Identifying Model Misconfigurations with AI-SPM
The broad range of models used across development, testing and production environments creates a need for visibility and control. Amazon Bedrock centralizes model deployment and management, giving organizations a dedicated, managed service to deploy AI in your environment. Centralizing these services makes it easier to track which models are in use, who has access to them, and how they're being utilized. Additionally, Custom Model Import (currently in preview) can be used to import weights for fine-tuned or modified models stored in your AWS account.
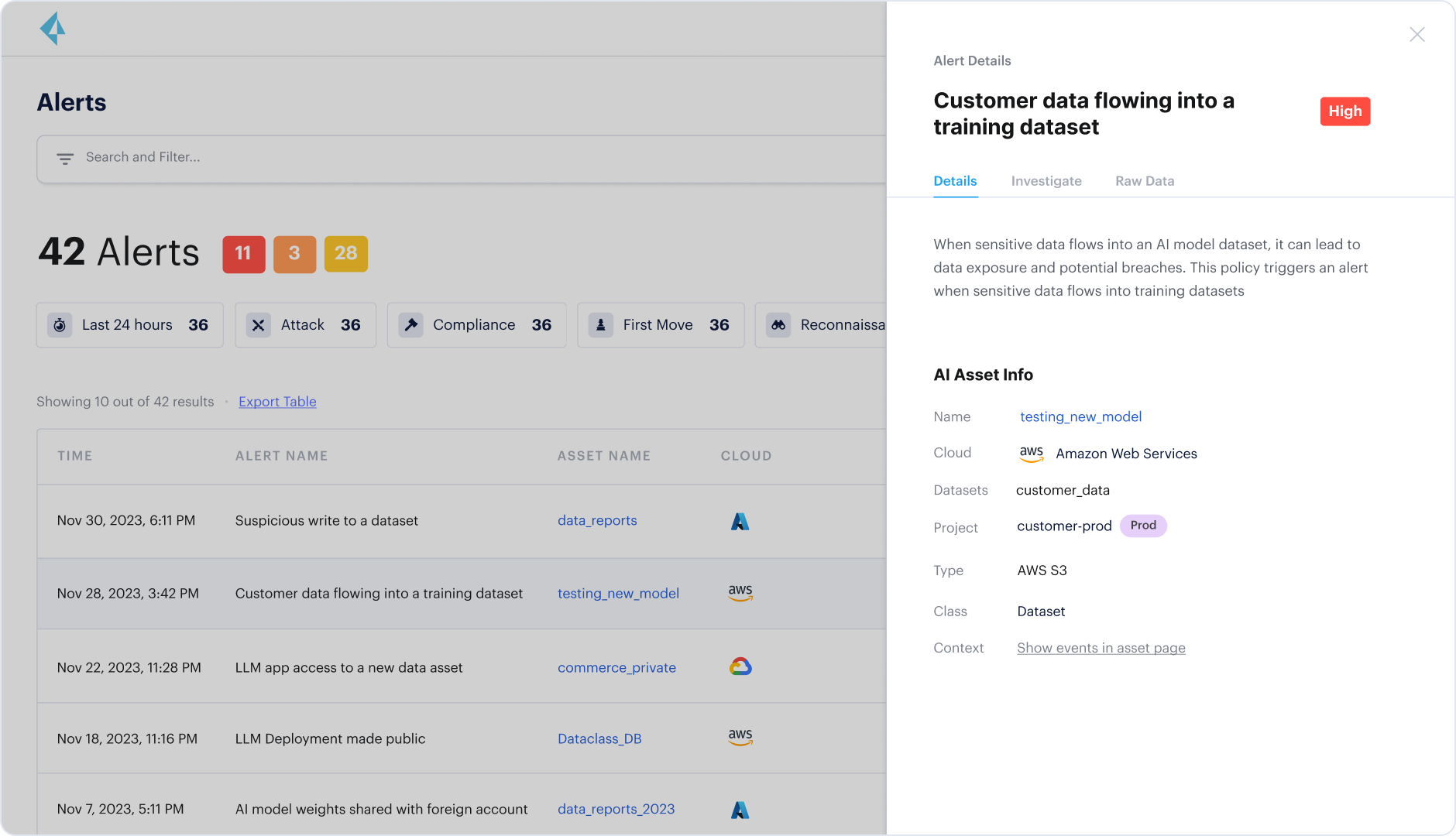
Complementing this, Prisma Cloud AI-SPM enables you to see which models are deployed in your cloud environment — whether via Bedrock or other APIs — and identify risks related to the data used for training or fine-tuning. For instance, Prisma Cloud might detect a publicly accessible AI-powered chatbot fine-tuned on sensitive data. Or it could identify model weights stored on S3 and ensure protections are applied to prevent supply chain attacks.
Protecting the Application Layer
Avoiding post-deployment attacks on AI applications is the final piece of the puzzle. Amazon Bedrock Guardrails makes it easy to monitor prompts sent to LLM APIs, helping to prevent prompt injection attacks and other misuses. Organizations can tailor the guardrails to their use case and risk tolerance, enabling them to set up content filtering, implement input validation and control model outputs.
Prisma Cloud complements this by identifying AI assets that lack sufficient security controls or safety tools, such as models deployed without content filtering. The proactive approach allows security teams to address vulnerabilities before they’re exploited, with Bedrock Guardrails providing an additional layer of control.
Build Your AI Applications with Security at the Core
Organizations can’t afford to fall behind in the race to production AI, nor can they compromise on critical security features. By combining Prisma Cloud's comprehensive visibility and risk analysis with Amazon Bedrock and Amazon Bedrock Guardrails, they can confidently build and deploy AI applications, knowing they're protected from data to model to deployment.
Next Steps
- Download AI Governance for AI-Powered Applications to learn how to establish a governance framework for your AI-powered applications.
- Visit the Prisma Cloud website to learn more about Prisma Cloud AI-SPM.
- Explore Prisma Cloud offerings on the AWS Marketplace.
- Check out Amazon Bedrock and Amazon Bedrock Guardrails.