How SD-WAN helps Today’s IoT
SD-WAN technology enables businesses to manage devices and networks programmatically instead of manually. In addition to its benefits in securely connecting remote users in branch offices, SD-WAN is valuable in controlling IoT devices over global networks. Overall, SD-WAN can help today's IoT by providing a more efficient and secure network infrastructure that can handle the increasing volume of data generated by IoT devices.
What Is SD-WAN?
SD-WAN, or software-defined wide area network, is technology that uses software to flexibly manage and optimize the performance of wide area networks. It offers the reliable connectivity that enterprises need to securely connect their data, applications and users across branches and regions. And for infrastructure teams, it provides simpler, centralized control of the WAN with better visibility, telemetry and reporting.
Traditional WANs rely on hardware such as routers to manage network traffic. Network administrators and engineers manually write rules and policies to define the flow of traffic between remote users and the applications hosted in data centers. SD-WAN replaces those manual, error-prone processes with software that configures the network in real time to handle different kinds of traffic and conditions. The improved flexibility means greater security, higher reliability and better application performance than traditional WANs can provide.
Software-based networks require fewer hardware devices at each location, which simplifies connectivity and reduces cost. Networking teams can implement and reconfigure their wide area networks remotely, without adding hardware, as the needs of the business change.
How Does Current IoT Deployment Work?
Although IoT adds efficiency and control through edge computing, it also greatly expands the attack surface. Most IoT devices are strong on connectivity and weak on security (think baby monitors and automated home lighting). They introduce vulnerabilities through the potential to smuggle malicious IoT data that corrupts the smooth functioning of the device and compromises the networks to which it's connected. Additionally:
- IoT is challenged to keep pace with transformation, especially in branch offices. Zero visibility and unknown vulnerabilities expose the network to several types of IoT breaches.
- Unencrypted internet connections can be easily exploited by hackers, allowing them to gain access to IoT devices, systems and data. This can lead to theft of proprietary information, financial losses and other security risks.
- Unsupported operating systems no longer receive security updates, leaving them vulnerable to malicious attacks. They also risk incompatibility with newer software and hardware.
The increased risk of ransomware imperils connected devices and networks, such as home security systems, smart appliances and medical devices. If a ransomware attack results in a lockdown, entire systems can be rendered inaccessible until a ransom is paid.
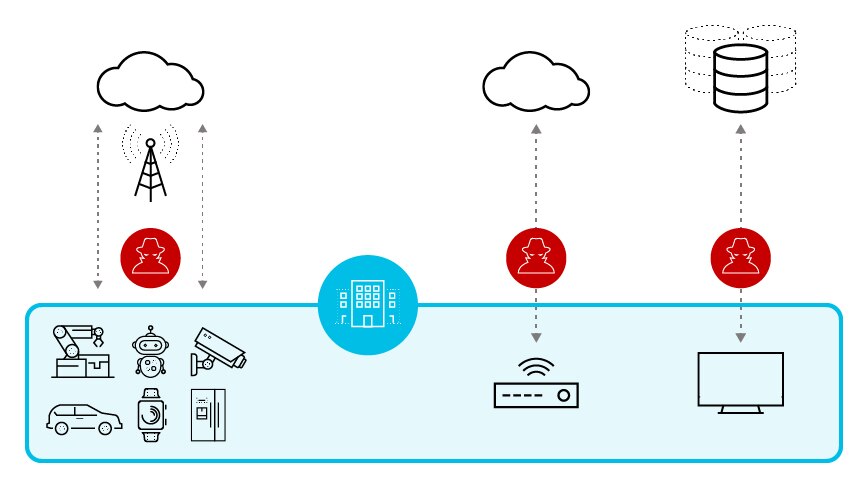
The hardest part of monitoring any network is ensuring that all devices are visible. That applies particularly to IoT and industrial IoT (IIoT) devices because their number, complexity and wide distribution make it hard to measure network performance accurately.
The fact is that the traditional approaches to securing IoT systems have proven ineffective. And attempts to overcome the challenges around IoT breaches have only added complexity to current deployments. For example, some companies introduce point products like IoT sensors, but those simply generate more data; they don’t enhance security. Other companies backhaul all branch traffic for central inspection, which thwarts IoT’s essential goal of decentralization and edge computing. Another option is network isolation and shutdown of IoT devices when threats are detected, but that entails yet another layer of monitoring and maintenance.
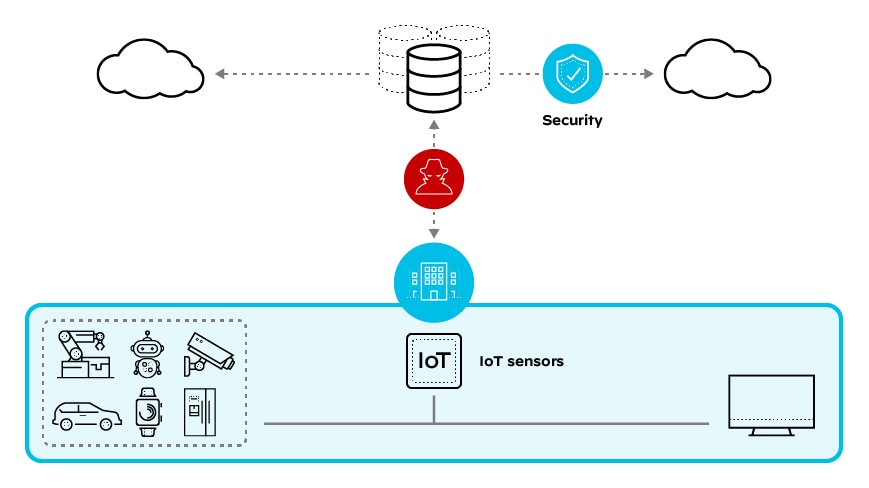
How Does SD-WAN Help Today’s IoT?
In the era of the internet of things, the proliferation of IoT devices is continually extending enterprise networks. The concept of the network edge has evolved to encompass not only the devices themselves, but also IoT sensors and the data they generate.
Even as IoT deployments push the boundaries of the network to the realms of vehicles, manufacturing equipment and wearable devices, networking teams need to centralize control and see their landscape through a single pane of glass.
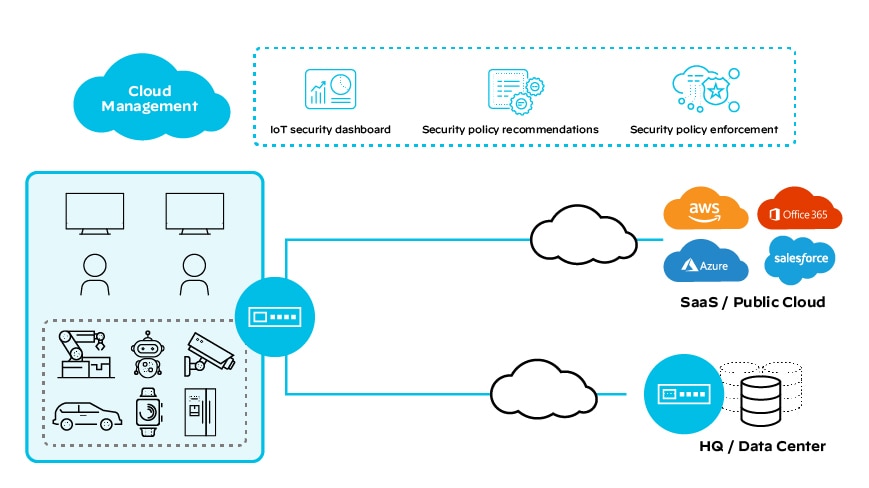
SD-WAN solutions are well suited for meeting the connectivity needs of a rapidly growing population of IoT devices. In the same way that standard networks benefit from software-defined operation, IoT networks benefit from the performance monitoring, aggregation, real-time routing and path selection of SD-WAN technologies.
Elements of an SD-WAN Platform
By virtue of the security and ease of device management that SD-WAN brings, enterprises exercise greater control over their global networks with less work. SD-WAN enables network administrators to manage even their most remote endpoints centrally, which makes traffic management easier and mitigates the risk of network outages.
To derive the greatest benefit from SD-WAN solutions, here are three essential ways that software-based wide-area technologies help in enterprise-wide IoT deployments.
Increasing Visibility
The growth of IoT leads networking teams to pursue a swivel-chair approach to security in which they dart from one tool and screen to another, attempting to cobble together a full picture of their network landscape.
Cloud administration and management of SD-WANs is the most effective way to achieve real-time insight into how devices are behaving and the network is performing. The cloud centralizes the full overview of network status and empowers network administrators to keep data from IoT sensors moving smoothly.
Maximizing Security
Software-defined networks maximize IoT security with protection from external threats like DDoS attacks and malware. They are also designed to mitigate internal threats because it grants access only to authorized IoT devices. It automatically blocks access to unapproved IoT devices, data and locations.
SD-WAN solutions bolster the efforts of network administrators and security teams accustomed to securing traditional computing equipment. They are flexible enough to find non-traditional devices anywhere on the network and bring them under the umbrella of enterprise-caliber security. They dynamically apply policies from centralized cloud or on-premises sources for the anti-spyware, web filtering, anti-malware and antivirus protection needed to defend a network with a vast attack surface.
Continuous Adaptation
It's hard enough for networking teams working on hardware to create, implement and test rules for typical enterprise devices. Protecting new IoT categories of devices is yet another burden on already stressed teams.
Software-based SD-WAN is better suited to handle the different kinds of traffic and conditions of IoT. It is designed for quick, continuous adaptation to the ever-changing threat landscape, and it offers more reliable security than traditional WANs. Instead of forcing IoT devices to depend on their connection to the data center, SD-WAN connects them to cloud resources. It replaces static, hardware-bound routes with application-aware, software-defined routes that respond to network congestion and keep data moving with minimal latency.
Benefits of SD-WAN Capabilities for IoT
As the IoT wave breaks on the shores of the enterprise-wide network, the SD-WAN is well suited to manage the flow of data from skyrocketing numbers of devices and connections. Enterprises that delay or dismiss the adoption of software-defined wide area networks are overlooking the time- and cost-savings that SD-WAN brings.
Moreover, as IoT continues to grow in importance in areas from agriculture to high-speed manufacturing, businesses will realize that their only hope for agility lies in efficient software.
Without expensive investments in new hardware, administrators can extend existing networks by deploying SD-WAN technologies close to where the IoT data is generated, no matter how far from the data center. The result is better performance and user experience for the greatly increased number of devices on the WAN.