What Is Secure SD-WAN? | What It Is and How It Works
The term "secure SD-WAN" describes an SD-WAN solution that integrates advanced security features with its core functionalities of optimizing and managing wide area network (WAN) connections.
Unlike traditional SD-WAN, which primarily focuses on improving network performance and connectivity, secure SD-WAN includes robust security measures to guard against cyber threats.
How does secure SD-WAN work?
The operational mechanics of secure SD-WAN (software-defined wide area network) are the same as those you can expect to find within a traditional SD-WAN architecture.
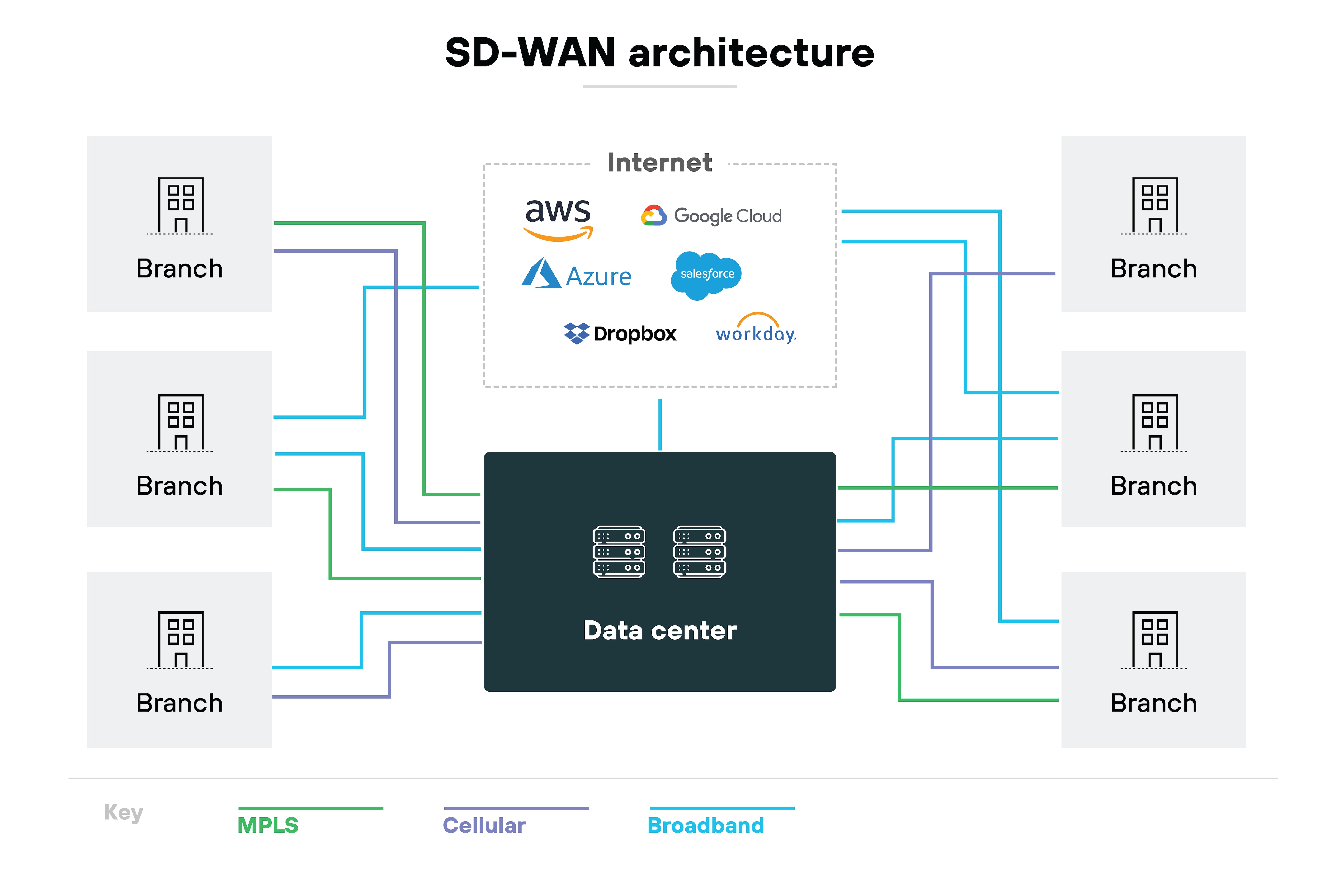
Secure SD-WAN operation begins with its ability to intelligently direct traffic flows across the WAN. Instead of sending all traffic through a central corporate data center—which can introduce latency and clog network bandwidth—secure SD-WAN uses policies to identify and route traffic through the most efficient paths.
It dynamically chooses between multiple connections, such as broadband internet, MPLS, or cellular links, based on the current network conditions and predefined policies, optimizing both performance and cost.
Like this:
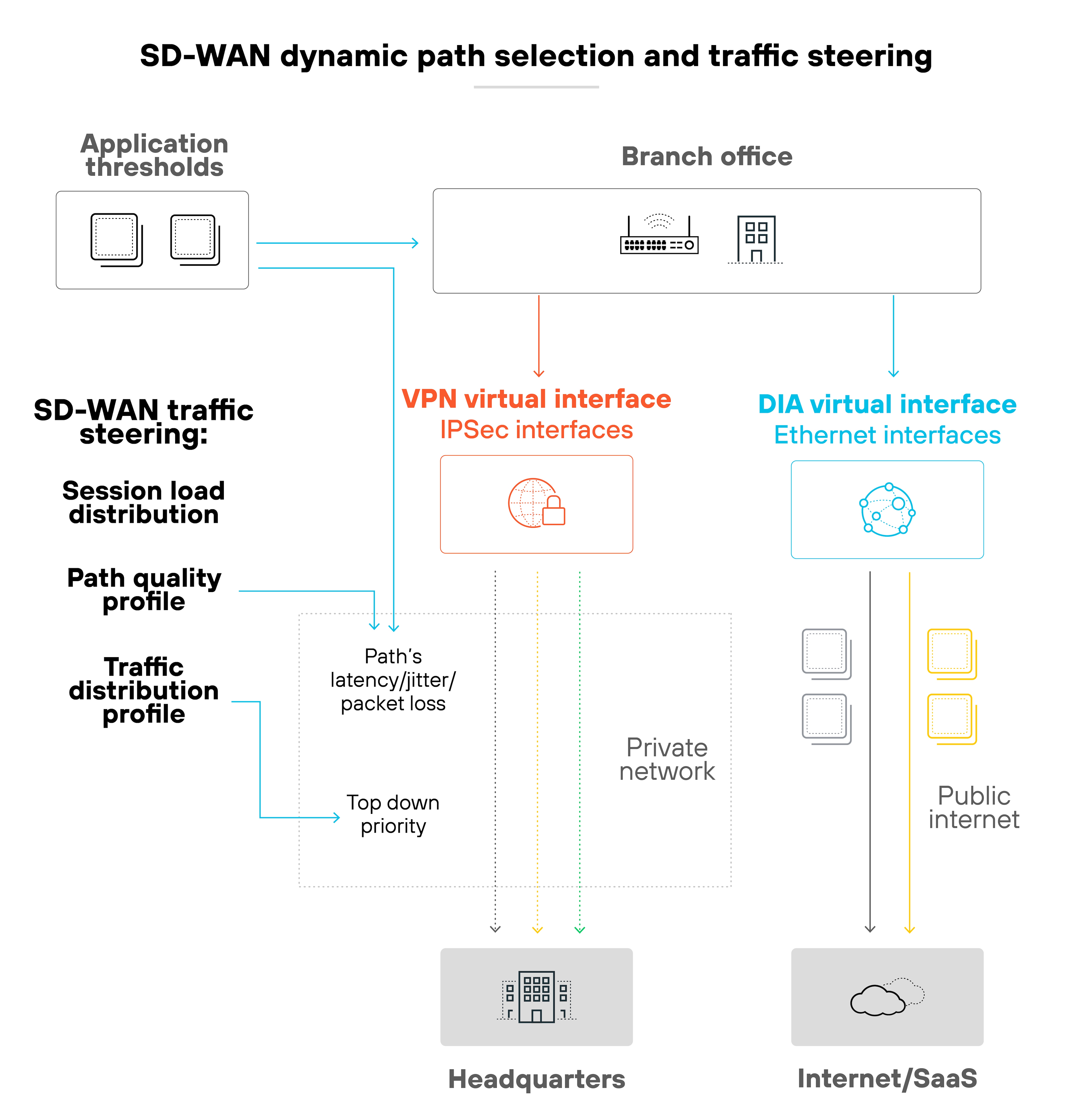
Now here’s where security comes in.
Security capabilities are woven into this fabric, with secure SD-WAN devices deploying next-generation firewall and intrusion prevention technologies at the branch level.
This setup ensures that sensitive data is encrypted and that all incoming and outgoing traffic flows are scrutinized for threats in real-time.
By integrating security into the SD-WAN devices themselves, organizations can enforce a consistent security posture across all locations. Which is way simpler and often more effective than managing disparate security products.
Here’s what it looks like:
Not to mention, secure SD-WAN is a great stepping stone for organizations who are seeking to increase security but aren’t yet ready for a full transition to a more comprehensive solution like SASE.
Further reading:
What are the common features of secure SD-WAN solutions?
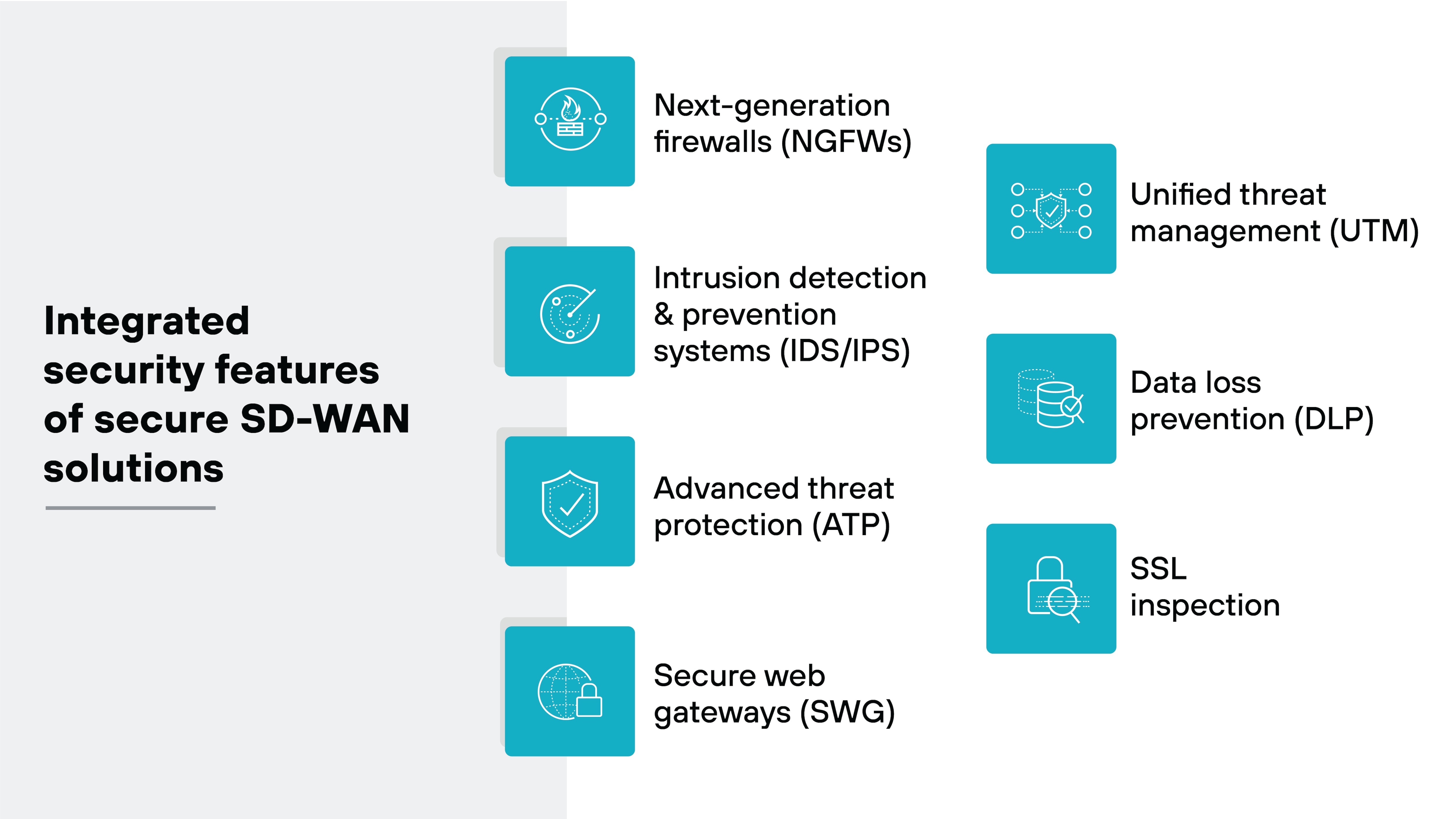
Secure SD-WAN solutions are fundamentally similar to traditional SD-WAN, incorporating all of the same core features, including:
- Internet connectivity
- Dynamic path selection
- Centralized management
- Quality of service (QoS)
- Application-aware routing
- Zero-touch provisioning
- Limited integrated security features
*Note: Security features depend on the SD-WAN solution and vendor.
As we’ve established, secure SD-WAN technology merges advanced networking capabilities with advanced security measures.
Integrated security features unique to secure SD-WAN solutions often include:
- Next-generation firewalls (NGFWs)
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS)
- Advanced threat protection (ATP)
- Secure web gateways (SWG)
- Unified threat management (UTM)
- Data loss prevention (DLP)
- SSL inspection
By offering these features, secure SD-WAN solutions improve network performance, streamline network management, and enhance network security.
Let’s take a closer look at each feature.
Next-generation firewalls
Firewalls play a key role in secure SD-WAN deployments by providing advanced security features integrated into the network fabric.
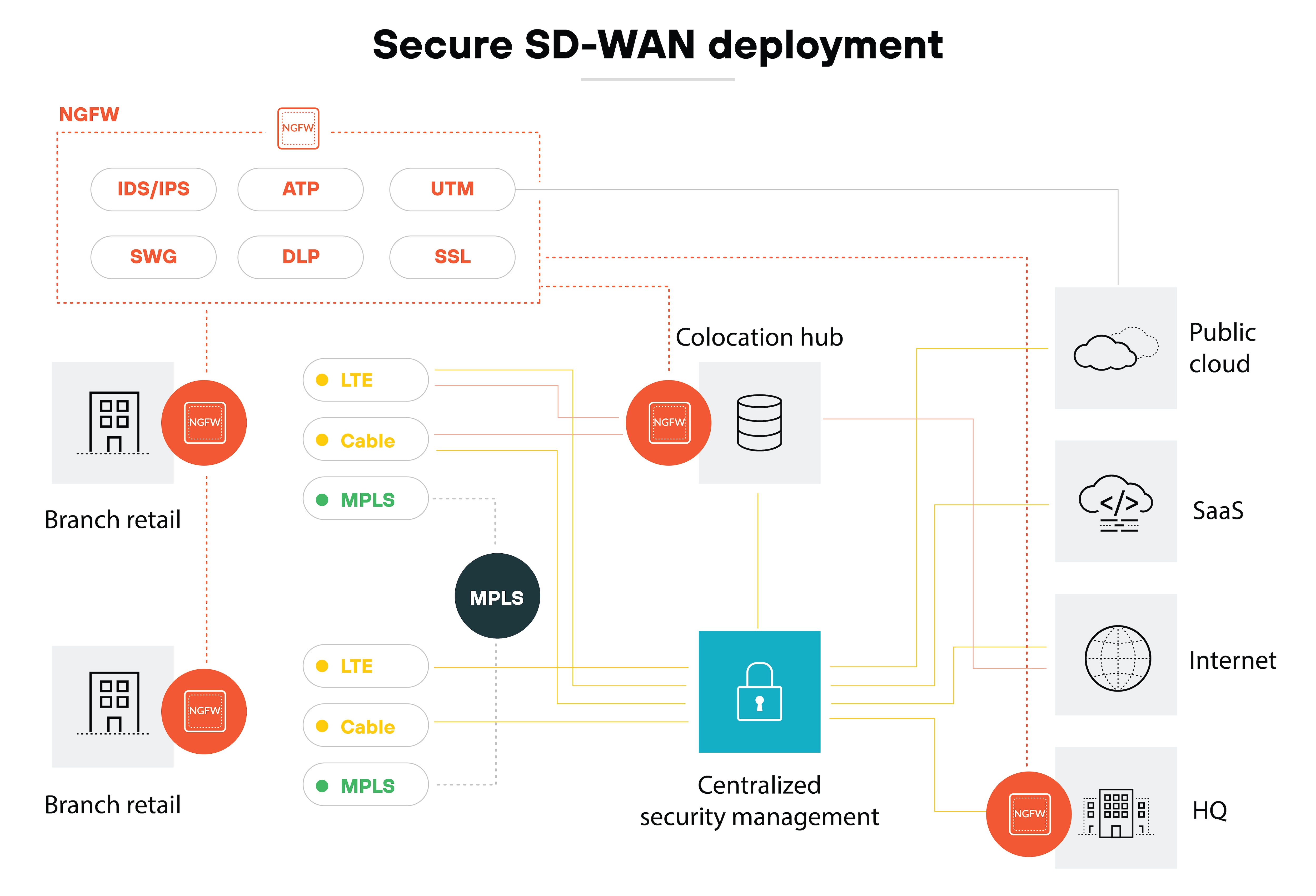
In secure SD-WAN architectures, NGFWs are deployed at branch locations and headquarters, serving as a first line of defense against cyber threats.
Here’s what it looks like:
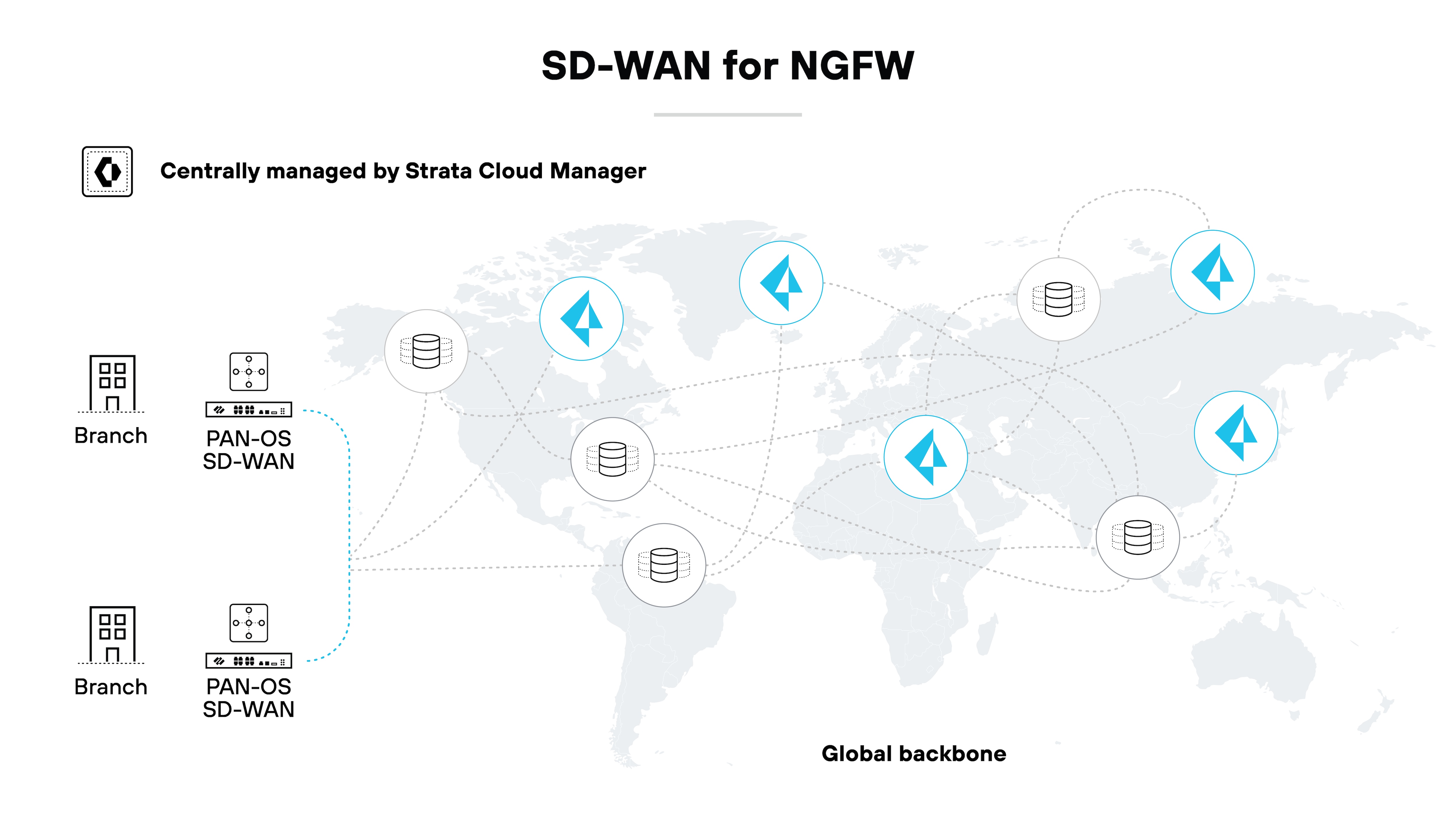
This particular scenario demonstrates the integration of Palo Alto Networks NGFWs into an end-to-end Prisma SD-WAN architecture, architected for global interconnect. The end result is natively integrated security and connectivity. Note: Deployments vary depending on the SD-WAN and NGFW solutions, as well as the network environment.
NGFWs offer enhanced capabilities including but not limited to:
- Application awareness
- URL and web content filtering
- Deep packet inspection
- Malware detection
- Antivirus protection
A key function of NGFWs in secure SD-WAN is to enforce security policies consistently across all locations. This maintains the same level of security, whether users are accessing data from a branch office, headquarters, or through cloud based services.
Further reading: How Are Firewalls and SD-WAN Related?
Intrusion detection and prevention systems
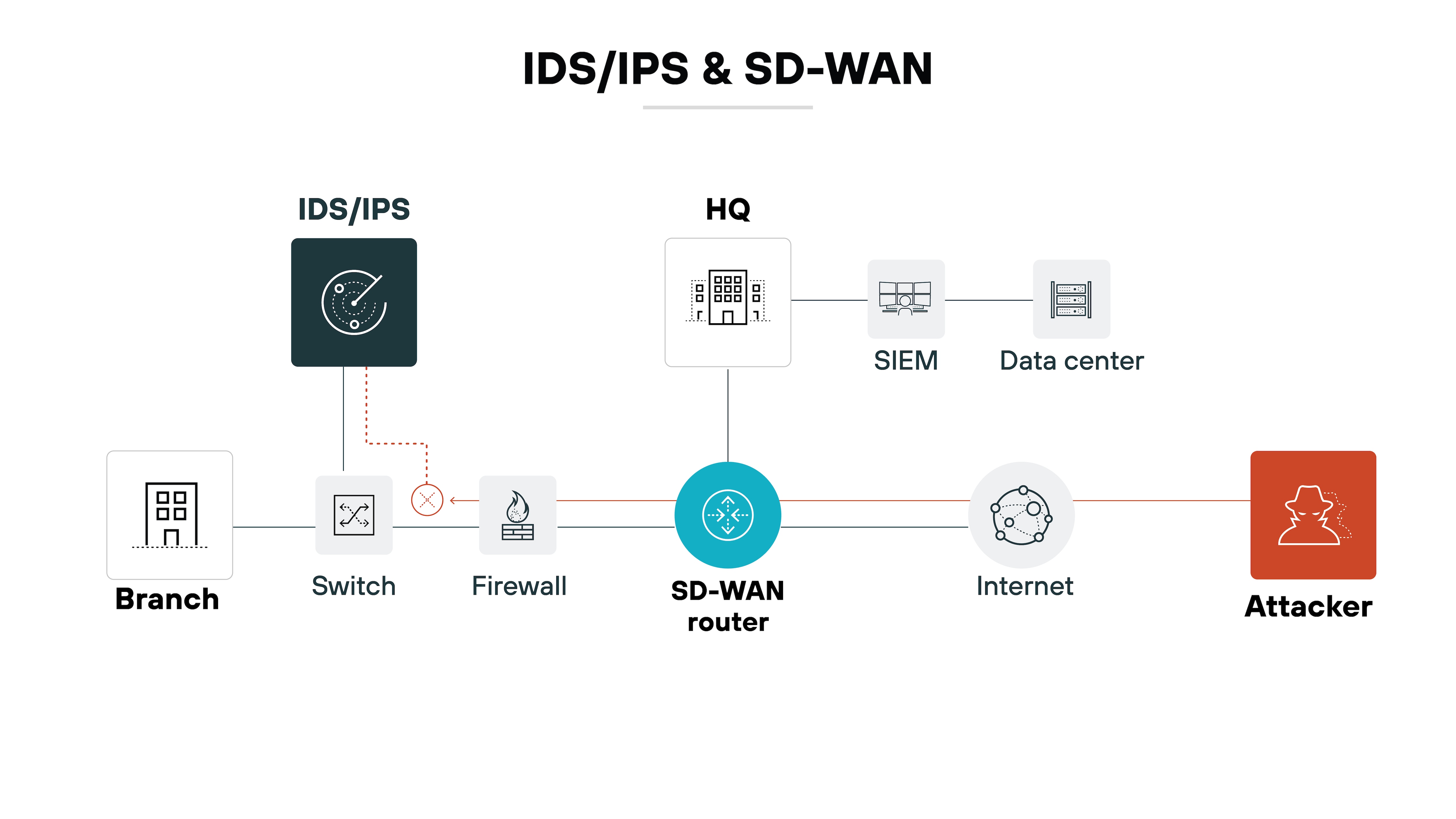
Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) are embedded within secure SD-WAN to monitor network traffic for signs of malicious activity and known threats, actively analyzing and preventing attacks.
Advanced threat protection
Advanced threat protection offers sophisticated defenses against evolving cyber threats by using continuously updated threat intelligence to identify, block, and remediate attacks in real time.
These defenses include, but aren’t limited to:
- Sandboxing
Sandboxing provides a controlled environment to execute suspicious code or analyze unknown software. This helps in identifying zero-day threats by observing behavior without risking the main network. - Encrypted traffic analysis
Encrypted traffic analysis allows for the detection and blocking of threats within encrypted traffic without decryption, maintaining privacy while reducing load.
Secure web gateways (SWG)
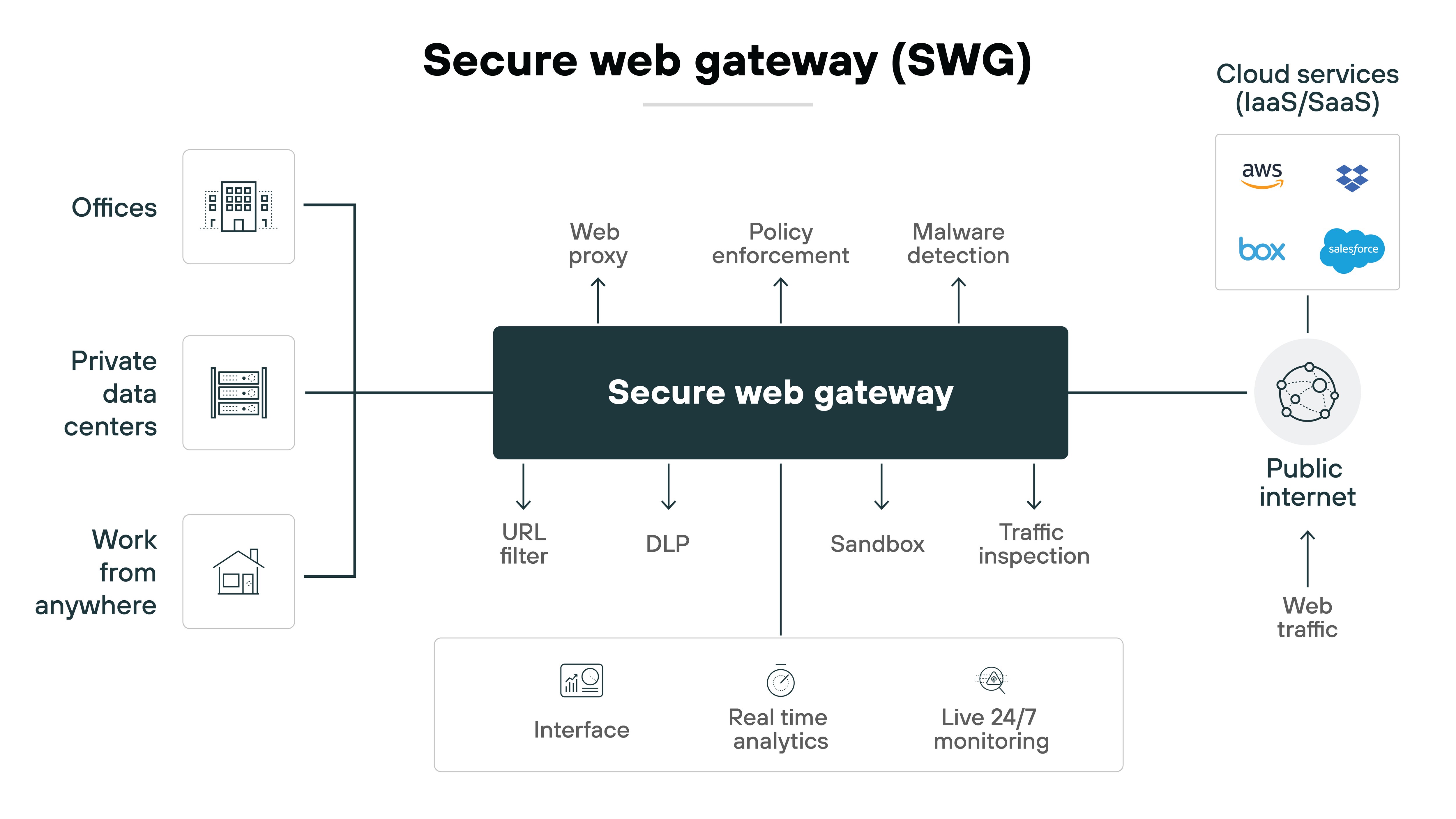
SWGs provide web security through content filtering, malicious website detection, and enforcement of corporate policies.
Data loss prevention
Data loss prevention (DLP) monitors and protects sensitive data from unauthorized access and breaches, ensuring it doesn’t leave the network without proper authorization.
SSL inspection
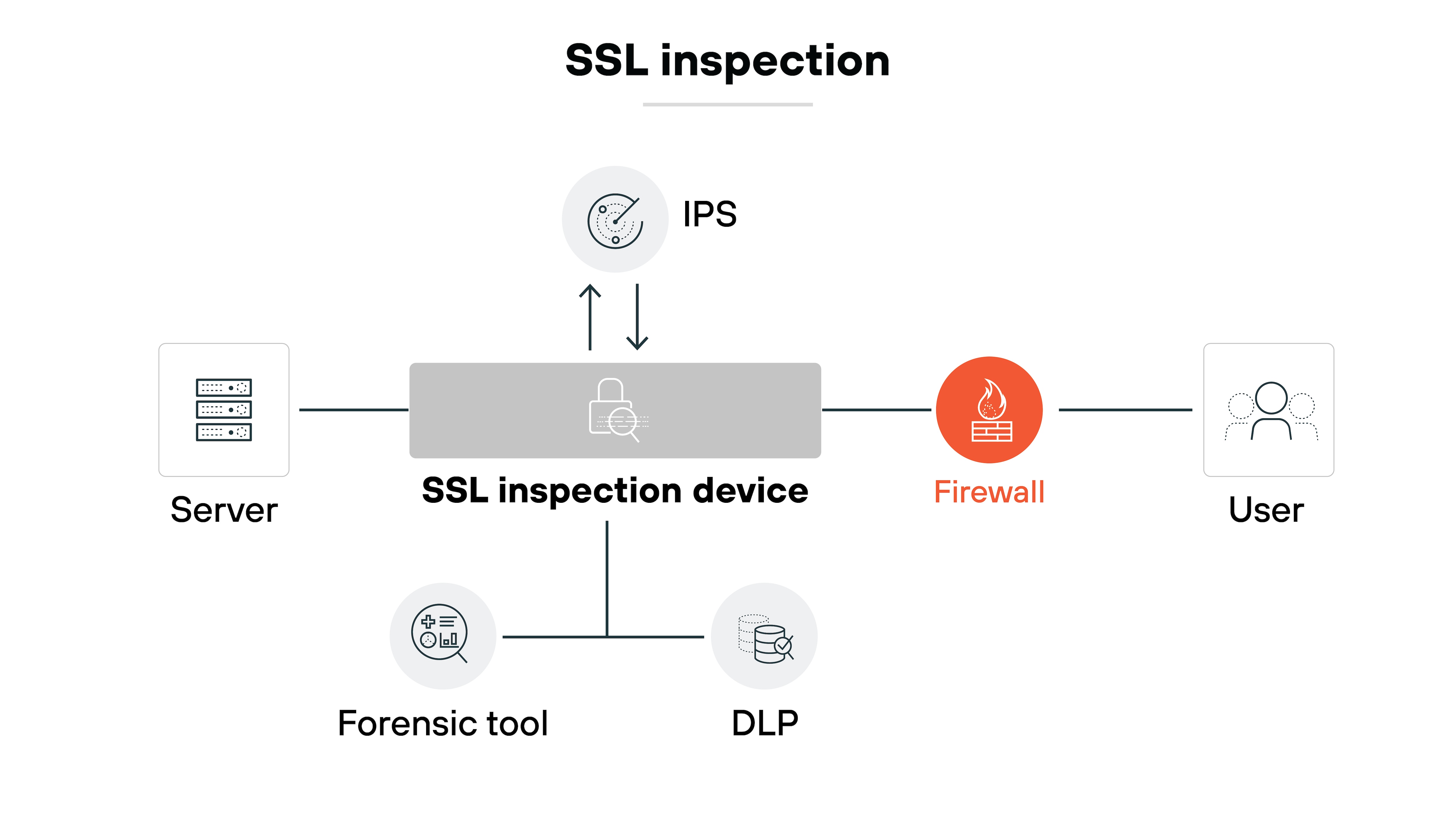
Secure SD-WAN solutions often include SSL inspection to decrypt encrypted traffic, enabling deeper inspection of the contents for hidden threats.
Unified threat management
Unified threat management (UTM) integrates essential security features into a single platform, several of which we’ve mentioned above, including:
- Antispam
- URL filtering and application control
- Firewalls
- IDS/IPS
- VPN
- Content filtering
What are the benefits of secure SD-WAN?
Secure SD-WAN offers the same foundational benefits of SD-WAN, including:
- Operational simplicity
- Carrier-independent WAN connectivity and improved ROI
- Improved security
- Enhanced performance
- Improved connectivity and direct cloud access
- Seamless connectivity management
- Foundation to secure access service edge (SASE) strategy
- Integration with other network services
- 24/7 support
- Hardware lifecycle management
- Public cloud support
Additional security benefits of secure SD-WAN solutions include:
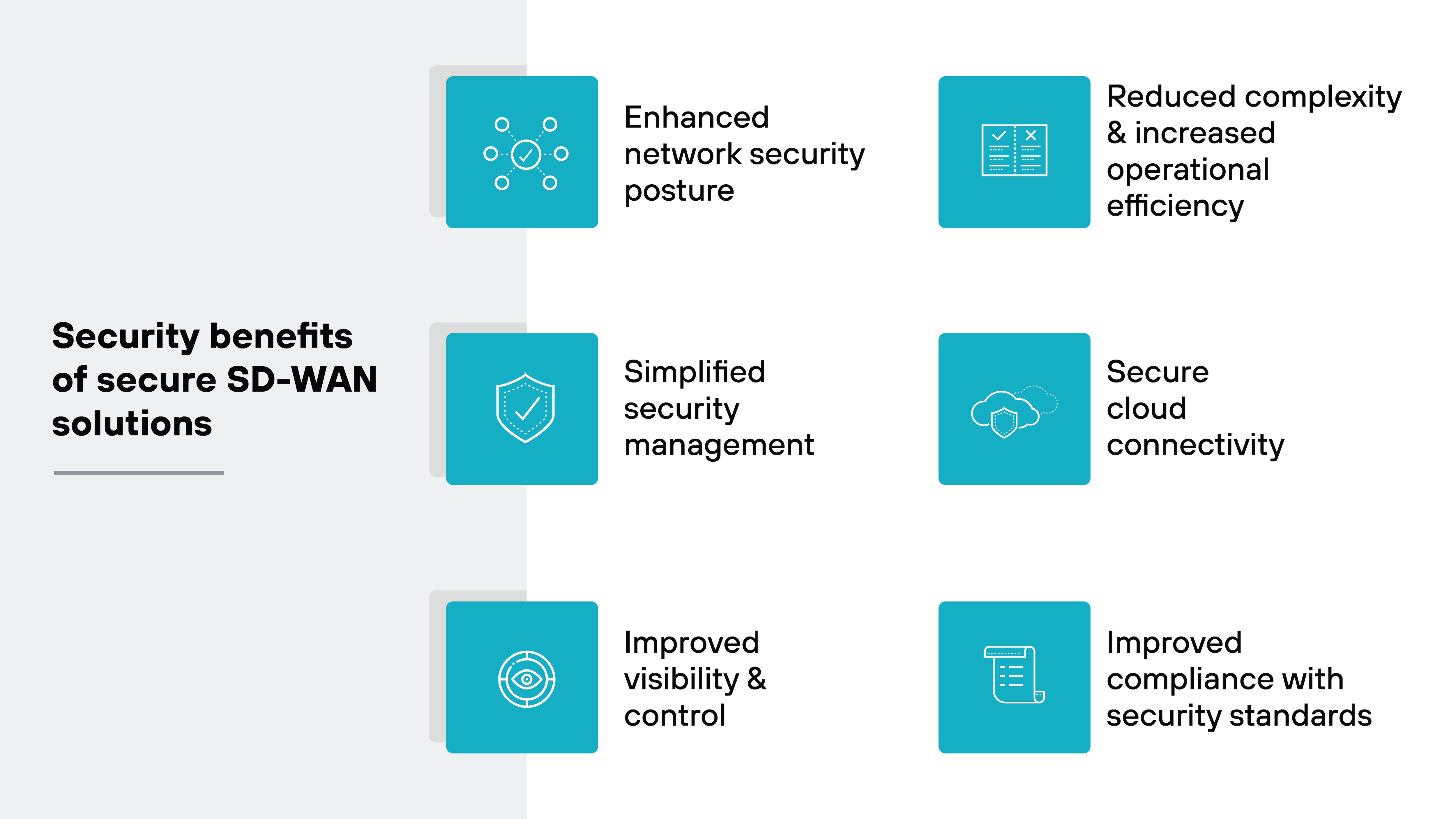
- Enhanced network security posture
- Simplified security management
- Improved visibility and control
- Reduced complexity and increased operational efficiency
- Secure cloud connectivity
- Improved compliance with security standards
Let’s dive into the details.
Enhanced network security posture
Secure SD-WAN improves overall network security posture by seamlessly integrating security measures into the network architecture. This approach ensures security isn’t just an overlay but built into the network. And that reduces the potential for gaps and vulnerabilities across the WAN.
Simplified security management
The centralized management capabilities of secure SD-WAN allow for streamlined security operations.
Like so:
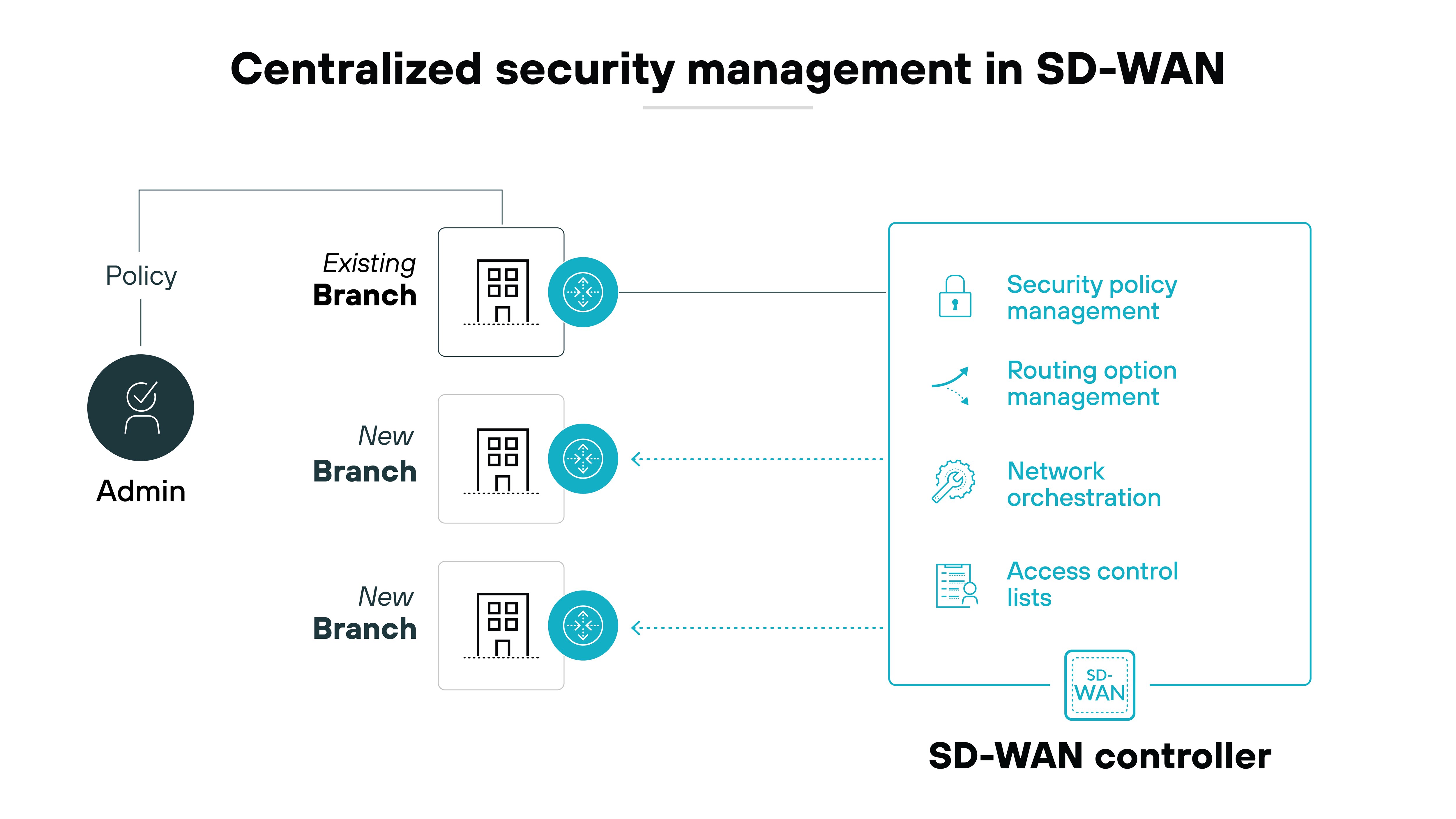
Network admins can implement and update security policies across all locations simultaneously. Which ensures consistent security measures are enforced without the need for manual configuration at each site.
Improved visibility and control
Secure SD-WAN solutions also provide enhanced visibility into network and application traffic with detailed analytics and reporting capabilities.
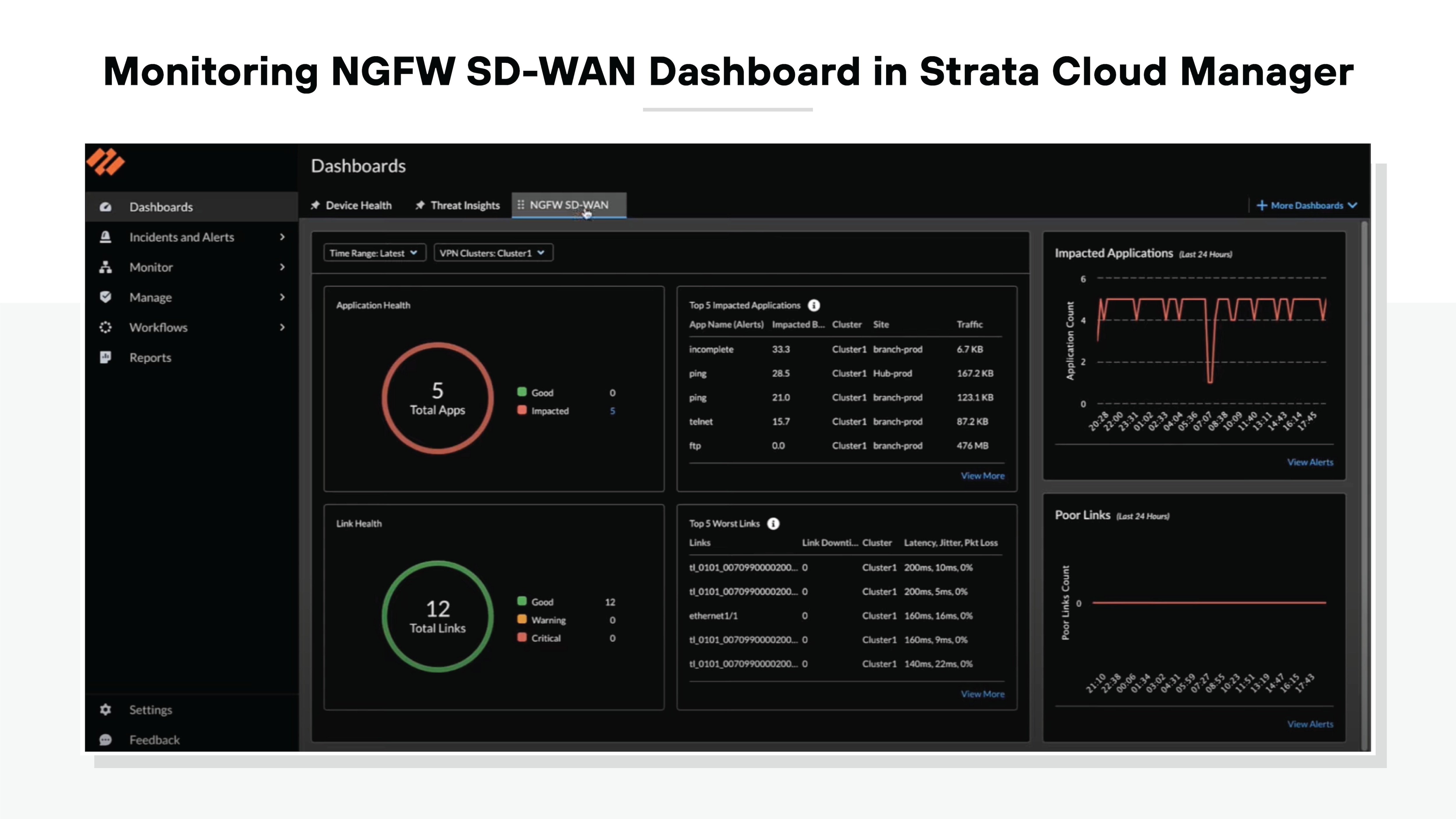
Here you can see an example of the NGFW SD-WAN Dashboard in Strata Cloud Manager, which allows you to monitor network traffic, manage security policies, and view real-time analytics from a centralized platform. Note: Security analytics and reporting capabilities will be different depending on the SD-WAN vendor.
The visibility ensures security teams can better understand traffic flow patterns and potential threats. This allows for quicker responses to security incidents and more informed decision-making overall.
Reduced complexity and increased operational efficiency
Integrating security functions with SD-WAN reduces the complexity of network architectures.
The integration simplifies security management and streamlines operations. This way, IT teams can focus on strategic tasks rather than maintaining multiple disparate systems.
Secure cloud connectivity
Secure SD-WAN facilitates efficient, secure connectivity to cloud applications.
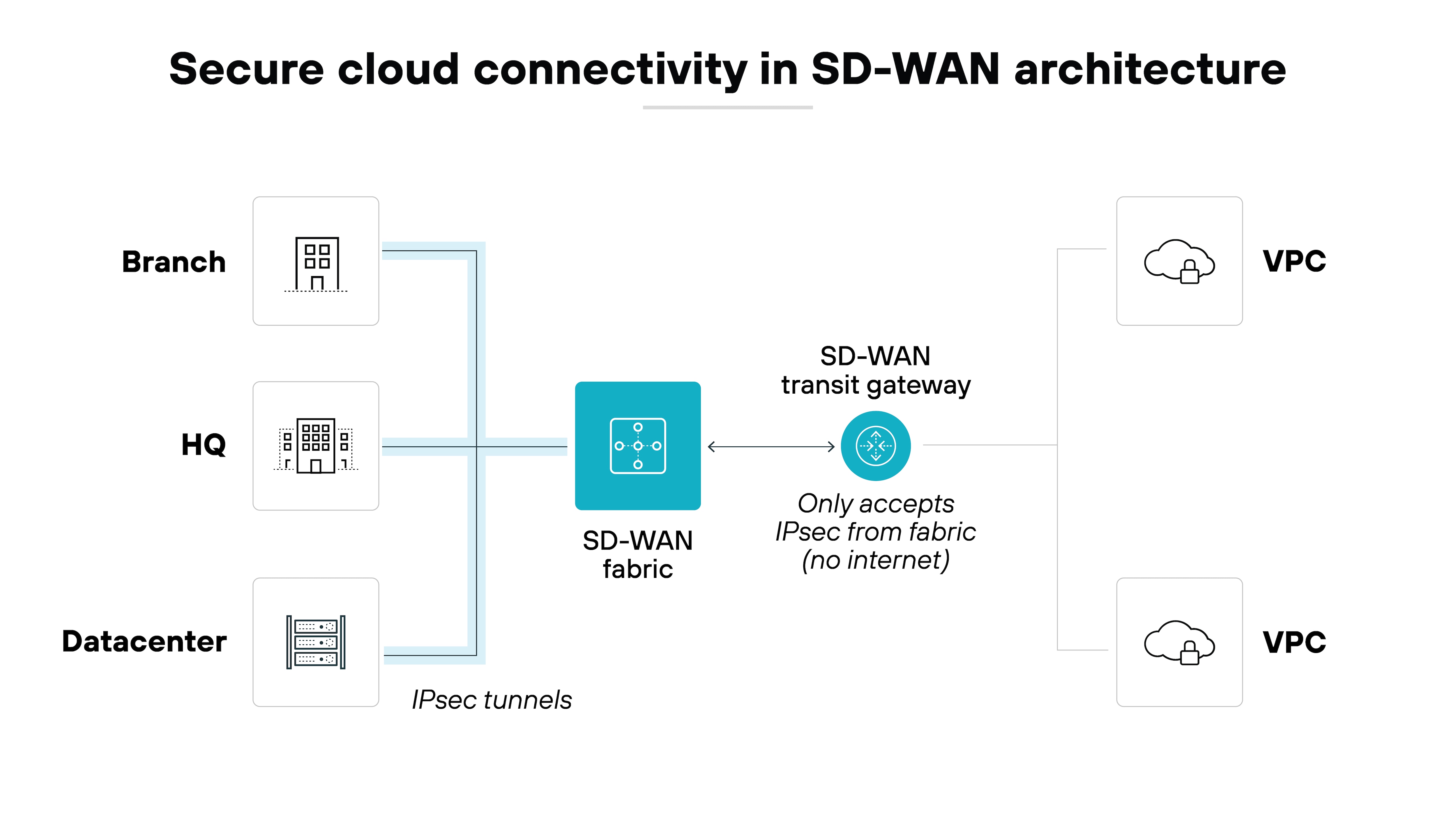
Data remains protected as it travels across the internet and into cloud services. Which is especially important for organizations who relying on a large number of SaaS applications—because of the robust security measures we reviewed earlier directly within the SD-WAN solution.
Further reading: What Is SD-WAN Multicloud?
Improved compliance with security standards
Secure SD-WAN also facilitates easier compliance with regulatory requirements and security standards.
Since secure SD-WAN solutions maintain high levels of security across all network segments and endpoints, organizations can meet stringent compliance demands more efficiently.
Who should consider secure SD-WAN?
- Organizations replacing outdated security infrastructure are often good candidates for secure SD-WAN.
For companies aiming to retire traditional branch firewalls and routers, secure SD-WAN offers a compelling upgrade.
Secure SD-WAN solutions usually integrate a multitude of advanced security capabilities. Which gives organizations the opportunity to seamlessly replace legacy equipment while securing untrusted links with IPsec tunnels and enforcing consistent policies across the WAN. - Businesses who want to simplify branch architecture securely can benefit from evaluating secure SD-WAN solutions.
![SD-WAN architecture diagram which depicts connecting multiple branch sites to various cloud applications and a central data center. The layout shows several branch icons linked by lines in different colors representing different types of connections: MPLS, cellular, and broadband, as indicated by the key at the bottom. Cloud services such as AWS, Google Cloud, Azure, Salesforce, Dropbox, and Workday are shown above the central data center, connected to it via the internet. The connections are visualized as solid and dashed lines, denoting direct and internet-mediated links.]() Secure SD-WAN facilitates centralized security orchestration. That makes it easier for companies with multiple branches to enforce uniform security measures.
Secure SD-WAN facilitates centralized security orchestration. That makes it easier for companies with multiple branches to enforce uniform security measures.
This is crucial for enterprises looking to maintain stringent security standards across geographically dispersed sites without the complexity and overhead of managing numerous individual devices. - Companies planning for secure, cloud-first approaches may also want to consider secure SD-WAN solutions.
Secure SD-WAN's ability to intelligently direct traffic comes in handy when it comes to cloud services, enhancing security and performance.
It efficiently handles trusted SaaS and web traffic by directing it straight to the internet while routing unknown or untrusted traffic to appropriate security services. And that supports a cloud-first architecture without compromising security. - Organizations who are interested in increasing security and potentially transitioning to SASE in the future may want to consider secure SD-WAN solutions.
For organizations who are considering a move towards a secure access service edge (SASE) architecture but are hesitant to fully transition, secure SD-WAN offers a stepping stone.
![Architecture diagram titled 'Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)' showing the integration of networking and security services. At the top, four icons represent different cloud environments: SaaS Applications, Public Cloud, Private Cloud, and HQ/Data Center. Below, a horizontal bar labeled 'Security as a Service Layer' includes five components: FwaaS, CASB, ZTNA, and Cloud SWG. Another bar labeled 'Network as a Service Layer' contains SD-WAN. The bottom section shows three icons representing different locations: Branch/Retail, Home, and Mobile, connected by a red horizontal line. The diagram illustrates how SASE integrates security and networking services across various environments and locations.]()
It provides foundational elements of SASE, such as improved security and network efficiency, without requiring a complete overhaul of existing network infrastructures. This allows businesses to gradually integrate SASE components at a pace that suits their readiness and budget.
What is the difference between secure SD-WAN and SD-WAN security?
"Secure SD-WAN" and "SD-WAN security" are terms that often appear together but represent distinct concepts within the domain of network management.
Both terms focus on the security of SD-WAN networks. Essentially, secure SD-WAN is inherently security-focused with integrated solutions, while SD-WAN security is more about the application of various security strategies to protect the network.
Secure SD-WAN refers specifically to SD-WAN solutions that are designed with integrated security features from the outset. Again, this design philosophy ensures security is not an afterthought but a fundamental component of the network architecture.
SD-WAN security pertains to the security measures and protocols implemented to protect the integrity and data of an SD-WAN network. The term can mean different things to different people, but this generally involves integrating additional security services or devices to enhance the security of an existing SD-WAN setup.
SD-WAN security can include adopting third-party security solutions—such as cloud-based security services or specialized security appliances—that work alongside SD-WAN technology to shield against external threats and vulnerabilities.
Further reading: What Is SD-WAN Security?

 Secure SD-WAN facilitates centralized security orchestration. That makes it easier for companies with multiple branches to enforce uniform security measures.
Secure SD-WAN facilitates centralized security orchestration. That makes it easier for companies with multiple branches to enforce uniform security measures.
